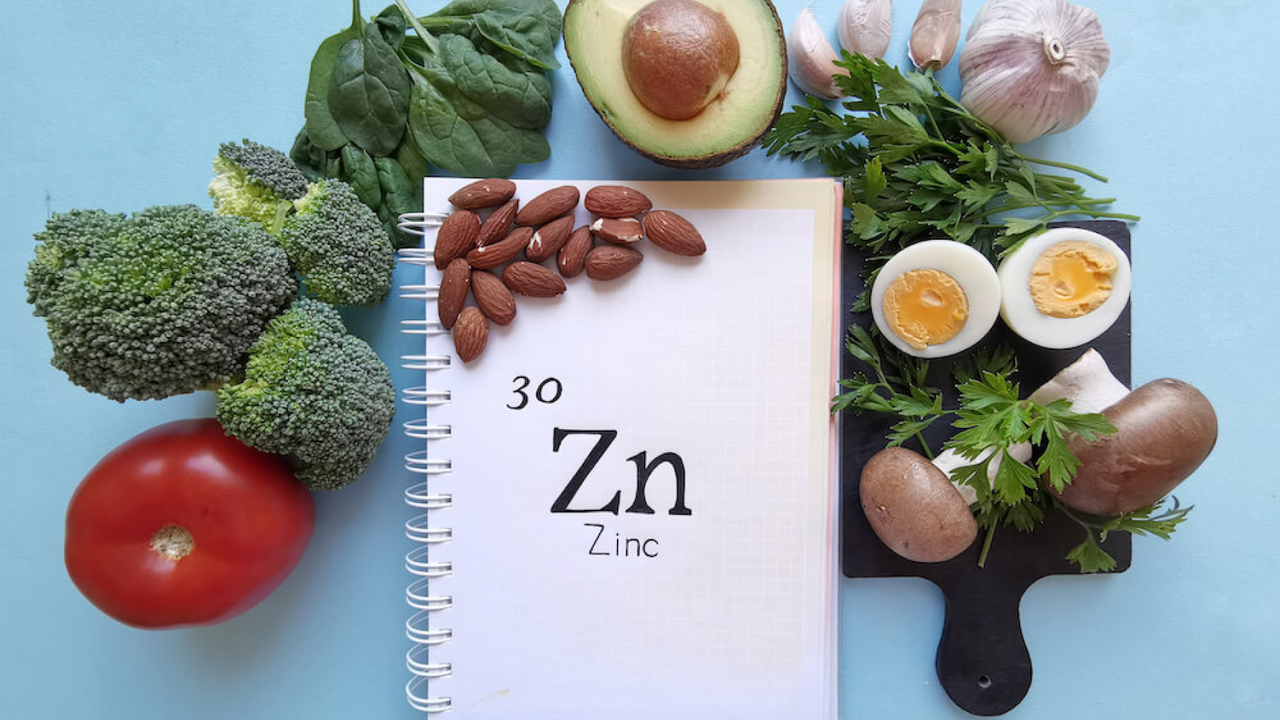Zinc (Zn) is a nutrient that plays a very large role throughout your body. There are many functions, health benefits, and uses. Mainly, for the purpose of this blog, topical use of Zinc can aid your immune system and is fundamental to skin health.
Immune system benefits of Zinc
Zinc is a mineral that your body depends on and uses in a multitude of ways. It is the second most abundant trace mineral in your body, and it is found in every cell. Zinc is vital in the function of over 300 enzymes that aid your metabolism, digestion, nerve function, and other processes. It is crucial for the evolution and behavior of the immune system and helps to keep your immune system strong. Zinc is widely used to treat colds, and there is some evidence that taking Zinc regularly can reduce the length of the common cold. Most recently, Zinc has been noted to aid the immune system in the fight against COVID-19.

Skin health benefits of Zinc
Zinc helps heal and rejuvenate skin by generating new cell production when the skin is broken to help fight against infection and inflammation and to close the broken skin. Zinc is less likely to irritate the skin because it does not absorb deeply, therefore you find zinc as a main ingredient in products for sensitive skin (such as products for babies and children). Zinc is quite beneficial in wound healing, and it is commonly used in hospitals and Doctor’s offices to treat rashes, ulcers, burns, and other skin injuries.
Zinc is found in baby diaper creams as a result of its quick healing capabilities, and it is also known to treat acne by reducing inflammation and suppressing oily glands.
Zinc is a naturally effective ingredient in sunscreen. It is a natural reflector of both UVA & UVB rays. When micronized using no-nano technology, it is the safest active ingredient to use in sunscreen. Non-nano Zinc particles have a controlled size that are unable to penetrate the skin.
How to naturally get Zinc?
Zinc is a nutrient your body does not store, so we must consume enough every day to ensure we are meeting suggested requirements. While there are plenty of Zinc supplements you can take, there are also ways to obtain zinc naturally, through food. The recommended daily amount of zinc consumption is 11mg for men and 8mg for women, 11 for women who are pregnant and 12 for breastfeeding women.
Eating a healthy and balanced diet that includes zinc enriched foods should satisfy everyone’s requirements. Some foods that you can add to your diet to supplement you zinc intake are:
- Meat – Bring on the steak because red meat contains the highest amounts of Zinc. Yum! However, large amounts of Red Meat have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease and some cancers. So, enjoy your steak, but not every night.
- Shellfish – Oysters, Crab, and shrimp are all good shellfish choices to add to your diet to contribute to your zinc intake.
- Legumes, i.e. chickpeas, lentils and beans – heating, soaking, or fermenting help improve legumes zinc absorption because legumes contain phytates. Phytates are antinutrients that inhibit the absorption of zinc and other nutritional minerals.
- Seeds – Always a great addition to your diet, seeds contain fiber, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals. Pumpkin, squash, and sesame seeds are particularly high in the mineral Zinc.
- Nuts – Cashews, almonds, peanuts and pine nuts are great additions to boost your daily Zinc intake. They are also a great snack to help reduce your risk for heart disease and diabetes.
- Dairy – Yum Yum! Who does love Cheese and Ice Cream?! Cheese and milk, specifically cheddar cheese, contain large amounts Zinc that can be absorbed by your body.
- Eggs – They say breakfast is the most important meal of the day, and here is another reason why that statement can be considered to be true. Eggs contain Zinc that can help you meet your daily target. While it is a moderate amount per egg, it is still a source of Zinc, and a healthy one at that.
- Whole Grains – Wheat, Quinoa, rice and oats are options that contain some zinc, but they also provide other health benefits that make them a great daily diet option.
- Certain fruits & vegetables like Potatoes, green beans, kale – Vegetables are always good for you. They do not contain large amounts of Zinc but they are linked to reduced risks of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
- Dark Chocolate – Bring on the nightly delight of a Dove or Ghirardelli square of dark chocolate! Dark Chocolate contains reasonable amounts of Zinc!
If you feel you may not be consuming enough Zinc through your daily diet, reach out to your healthcare provider about the possibility of taking Zinc Supplements.

Are most people deficient in Zinc?
It is estimated that about 20% of the world’s population is deficient in Zinc. Zinc deficiency is characterized by loss of appetite, growth retardation, and impaired immune function. People who are also deficient in Zinc also experience hair loss, weight loss, taste abnormalities, delayed healing of wounds, diarrhea, delayed sexual maturation, and some eye and skin lesions. People who are most at risk for Zinc Deficiency are:
- Vegetarians
- Pregnant & lactating women
- Infants who are older and exclusively breast fed
- Alcoholics
- People with gastrointestinal & other diseases
- People with Sickle Cell Disease
If you feel you have any of these symptoms, however, they may be a cause of another illness so it is important to seek out advice from your healthcare provider.
Zinc supplements? If so, what kind?
There are many Zinc supplements available in the marketplace, but some are better than others. Different types of Zinc impact your health and body in different ways. Some of the most common types of Zinc supplements you will find on the market are:
- Zinc Gluconate – Often used in cold remedies like lozenges and nasal sprays, Zinc Gluconate is the most common over-the-counter form of Zinc
- Zinc Sulfate – Used to help prevent Zinc deficiency, Zinc Sulfate is also used to reduce the severity of acne
- Zinc Picolinate – Zinc Picolinate has been noted to be a form of Zinc that your body may absorb better than other types of Zinc
- Zinc Acetate – Often added to cold remedies to reduce symptoms and speed up recovery
- Zinc Citrate – A well-absorbed Zinc supplement that has a less bitter, more appealing taste
- Zinc Orate – One of the most common types of Zinc found on the market today
Zinc supplements are available in capsule, tablet, and lozenge form. All forms are great options to get your daily dose of Zinc. Zinc Gluconate is the most cost effective and most commonly available form of Zinc to increase your intake without breaking the bank. If you have the ability to spend a little more, Zinc Picolinate is better absorbed by the body. We always recommend talking to your health care provider prior to taking Zinc supplements.
Summary
Zinc is a naturally safe & effective supplement for your immune system and your skin. There are many ways to increase your daily Zinc consumption, naturally and through supplementation. Make sure you are getting enough Zinc in your daily diet to ward off sickness. Add Zinc to your skin care regime to decrease the look of redness, fight acne, fight aging, and prevent sun damage.